Welcome to Classic Design Jewellers - Your custom design experts
The criteria used to evaluate diamonds as objectively as possible are referred to as the "4 Cs": Carat weight, Clarity, Color, and Cut.
The size of a diamond is critical to its value. The metric carat, which equals 0.20 grams, is the standard unit of weight for diamonds and most other gems. If other factors are equal, the more a diamond weighs, the more valuable it will be.
The clarity of a diamond refers to the amount, size, type and location of internal flaws (inclusions) or surface imperfections (blemishes) visible in a diamond using 10x magnification. All diamonds have imperfections in them. The "cleaner" the diamond, the higher the value. The following are several typical grades of diamond clarity:
FL= Flawless -- no internal or external inclusions of any kind visible under 10x magnification to a trained eye, the most rare and expensive of all clarity grades.
IF= Internally Flawless -- no internal inclusions visible under 10x magnification to a trained eye, but there may be some tiny external irregularities in the finish.
VVS-1= Very Very Slightly Included 1 -- usually just one tiny inclusion visible only to a trained eye under 10x magnification.
VVS-2= Very Very Slightly Included 2 -- tiny inclusions visible only to a trained eye under 10x magnification.
VS-1= Very Slightly Included 1 -- very small inclusions visible with 10x magnification.
VS-2= Very Slightly Included 2 -- several very small inclusions visible with 10x magnification.
SI-1 and SI-2 = Slightly Included 1 and 2 – noticeable inclusions that are easily seen under 10x magnification.
The following chart gives an idea how each grade might look under a 10x loupe microscope:

Chart courtesy of International Gemological Institute (IGI)
Grading color determines how closely a diamond's color approaches colorlessness. With the exception of fancy color diamonds, the colorless grade is the most valuable. If a diamond does not have enough color to be called fancy, then it is graded in a scale of colors ranging from Colorless to Light Yellow, "D" through "Z." A "D" color diamond is considered to be colorless. If the color is more intense than "Z," it is considered fancy. A fancy yellow diamond will sell for a far higher price than a light yellow diamond.
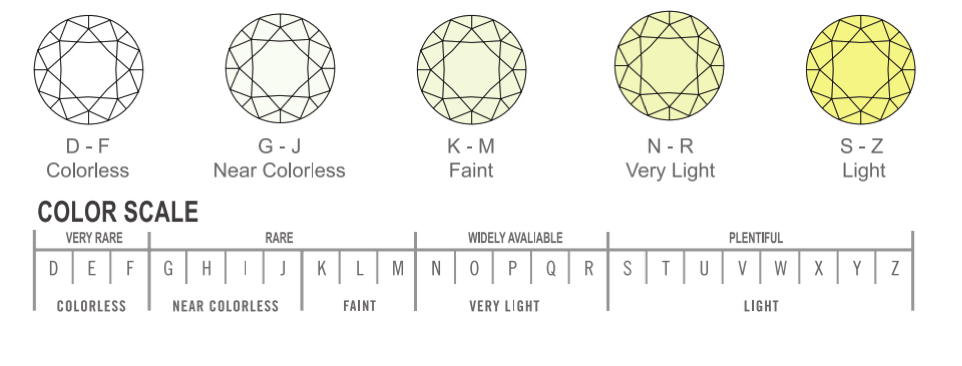
Chart courtesy of International Gemological Institute (IGI)
Cut or proportion is the only property of a diamond that is totally dependent on human intervention. Cut is important to consider when choosing a diamond as it alone affects the "sparkle."

Chart courtesy of International Gemological Institute (IGI)